Variables in DAX
As in any other programming language, you can also use variables in DAX. (But unlike in other languages, you don´t need them too much. It just makes the syntax little bit more clear.
Few more notes about variables in DAX:
- Variable can refer to other variable
- Variable cannot vary during calculation (so, honestly, it is not a variable…)
- Variables are calculated on the beginning – before the RETURN command – and can be used repeatedly. So they are calculated just once – which makes it quicker to calculate.
- Variable can contain single value or a table
The syntax is easy. We can define the variable, then write RETURN a normally continue with calculation.
Here we define a measure variable
- TotalSales =
VAR total_sales = SUM(‘original data'[Revenue])
RETURN
total_sales
And here we define a table variable
- ResultTable =
VAR mytable = FILTER(‘original data’;’original data'[Goods category]=”Fruit”)
RETURN
mytable
Practical variable use
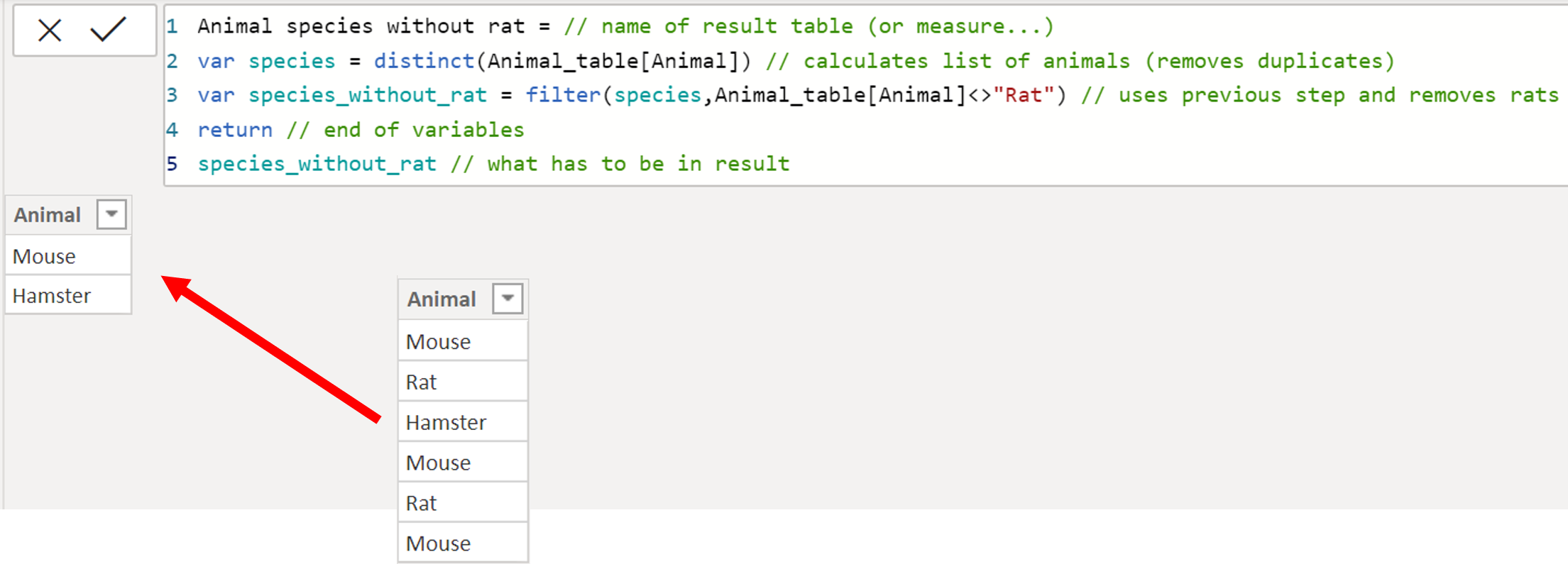
From original table, we are going to remove duplicates and then remove “Rats”.
FIrst option – calculates one variable, then another variable from the first variable, and then shows results
- Animal species without rat =
VAR species = distinct(Animal_table[Animal])
VAR species_without_rat = filter(species,Animal_table[Animal]<>”Rat”)
RETURN /
species_without_rat
Second option – calculates one variable and then calculates the result from it
- Animal species without rat =
VAR species = DISTINCT(Animal_table[Animal])
RETURN
FILTER(species,Animal_table[Animal]<>”Rat”)
![]()
![]()